It's hard to imagine that a 1,150 pound steer produces some 500 pounds of beef. That leaves 650 pounds of fluids, tissues, fats, and organs to be transformed into useful items essential to modern living. Thanks to Agricultural Research Service (ARS) scientists who think outside the box, important products used in food, medicines, and industry have been developed using beef by-products.
There are three categories of by-products to determine the items made with the rest of the animal: EDIBLE, INEDIBLE and MEDICINAL.
There are three categories of by-products to determine the items made with the rest of the animal: EDIBLE, INEDIBLE and MEDICINAL.
Edible By-Products
Some edible beef by-products are fairly well known such as variety meats. The nutritious value of liver, kidneys, brains, tripe, sweetbreads, and tongue has been acknowledged for quite a while. Other important edible by-products are less well known. Fats yield oleo stock and oleo oil for margarine and shortening. Oleo stearin is used in making chewing gum and certain candies. Gelatin produced from bones and skins is used in marshmallows, ice cream, canned meats, and gelatin desserts. Intestines may provide natural sausage casings.
Some edible beef by-products are fairly well known such as variety meats. The nutritious value of liver, kidneys, brains, tripe, sweetbreads, and tongue has been acknowledged for quite a while. Other important edible by-products are less well known. Fats yield oleo stock and oleo oil for margarine and shortening. Oleo stearin is used in making chewing gum and certain candies. Gelatin produced from bones and skins is used in marshmallows, ice cream, canned meats, and gelatin desserts. Intestines may provide natural sausage casings.
Inedible By-Products
You probably use at least one item containing inedible beef by-products every day. For example, you probably know that the beef hide is used to make leather, but did you know that the hide also supplies felt and other textiles? It provides a base for many ointments, binders for plaster and asphalt, and a base for the insulation material used to cool and heat your house. In addition, “camel hair” artists’ brushes are not really camel hair at all, but are made from the fine hair found in the ears and tails of beef cattle. Footballs, which used to be called “pigskins,” are also generally produced from cattle hide.
Industrial oils and lubricants, tallow for tanning, soaps, lipsticks, face and hand creams, some medicines, and ingredients for explosives are produced from the inedible fats from beef. Fatty acids are used in the production of chemicals, biodegradable detergents, pesticides, and flotation agents. One fatty acid is used to make automobile tires run cooler and, therefore last longer.
Bones, horns, and hooves also supply important by-products. These include buttons, bone china, piano keys, glues, fertilizer, and gelatin for photographic film, paper, wallpaper, sandpaper, combs, toothbrushes, and violin string.
You probably use at least one item containing inedible beef by-products every day. For example, you probably know that the beef hide is used to make leather, but did you know that the hide also supplies felt and other textiles? It provides a base for many ointments, binders for plaster and asphalt, and a base for the insulation material used to cool and heat your house. In addition, “camel hair” artists’ brushes are not really camel hair at all, but are made from the fine hair found in the ears and tails of beef cattle. Footballs, which used to be called “pigskins,” are also generally produced from cattle hide.
Industrial oils and lubricants, tallow for tanning, soaps, lipsticks, face and hand creams, some medicines, and ingredients for explosives are produced from the inedible fats from beef. Fatty acids are used in the production of chemicals, biodegradable detergents, pesticides, and flotation agents. One fatty acid is used to make automobile tires run cooler and, therefore last longer.
Bones, horns, and hooves also supply important by-products. These include buttons, bone china, piano keys, glues, fertilizer, and gelatin for photographic film, paper, wallpaper, sandpaper, combs, toothbrushes, and violin string.
Medicinal By-Products
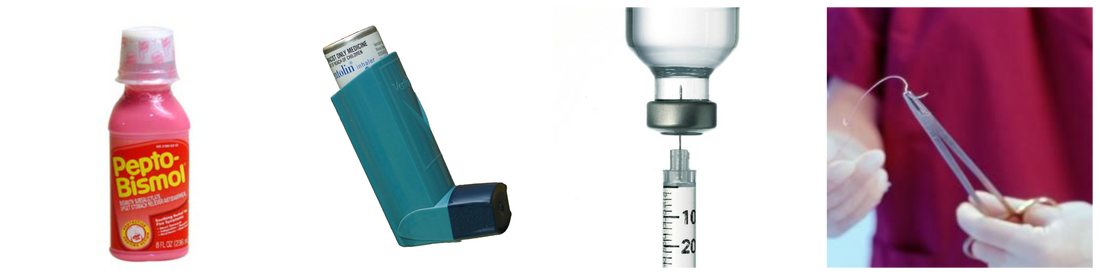
More than 100 individual drugs performing such important and varied functions as helping to make childbirth safer, settling an upset stomach, preventing blood clots in the circulatory system, controlling anemia, relieving some symptoms of hay fever and asthma, and helping babies digest milk include beef by-products. Insulin is perhaps the best-known pharmaceutical derived from cattle. There are 5 million diabetic people in the United States, and 1.25 million of them require insulin daily. It takes the pancreases from 26 cattle to provide enough insulin to keep one diabetic person alive for a year.
Whether using a traditional approach or innovative technology, everyone uses beef by-products daily. From life-saving medicines to improved safety on the highway, as well as clothing and helpful household items, we use every part of the cow exept the "moo".
More than 100 individual drugs performing such important and varied functions as helping to make childbirth safer, settling an upset stomach, preventing blood clots in the circulatory system, controlling anemia, relieving some symptoms of hay fever and asthma, and helping babies digest milk include beef by-products. Insulin is perhaps the best-known pharmaceutical derived from cattle. There are 5 million diabetic people in the United States, and 1.25 million of them require insulin daily. It takes the pancreases from 26 cattle to provide enough insulin to keep one diabetic person alive for a year.
Whether using a traditional approach or innovative technology, everyone uses beef by-products daily. From life-saving medicines to improved safety on the highway, as well as clothing and helpful household items, we use every part of the cow exept the "moo".


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed